🧪 "Crack the Code: Step-by-Step Solutions to NSSCAS Chemistry Past Paper 1 Exam Questions 2024 (With Expert Answers)"
Question: Acetophenone, C6H8O,
is an organic compound. What is the percentage by mass of hydrogen in
acetophenone?
Options:
A. 6.7 %
B. 8.0 %
C. 10 %
D. 22 %
Answer: A. 6.7 %
Explanation:
- The
molecular formula of acetophenone is C8H8O.
- The
molar mass of acetophenone is calculated as follows:
- Carbon
(C): 8 × 12 = 96 g/mol
- Hydrogen
(H): 8 × 1 = 8 g/mol
- Oxygen
(O): 1 × 16 = 16 g/mol
- Total
molar mass = 96 + 8 + 16 = 120 g/mol
- The
percentage by mass of hydrogen is:
Percentage of H = (8/120) × 100 = 6.7%
- A. 6.7%.
Question 2
Question: Which statement is correct?
Options:
A. 1.0 g of hydrogen gas contains 3.0×1023 atoms
B. 4.0 g of helium gas contains 1.2×1024 atoms
C. 16 g of methane gas contains 3.0×1024 atoms
D. 44 g of carbon dioxide gas contains 6.0×1023 atoms
Answer: C. 16 g of methane gas
contains 3.0×1024 atoms
Explanation:
We use:
- 1 mole
= 6.02 × 10²³ atoms/molecules
Let’s check:
- A: 1.0
g H = 1/1 = 1 mol → 6.02×10²³ atoms ❌
- B: 4.0
g He = 4/4 = 1 mol → 6.02×10²³ atoms ❌
- C: 16
g CH₄ = 16/16 = 1 mol → 6.02×10²³ molecules = 5 atoms × 6.02×10²³ = 3.01×10²⁴
atoms ✅
- D: 44 g CO₂ = 1 mol = 6.02×10²³
molecules ❌
✅ Answer: C
Question 3
Question: When 0.42 g of propanol reacts with
excess sodium, hydrogen gas is produced. What volume of hydrogen, measured at
room temperature and pressure, is produced?
Options:
A. 84 cm3
B. 168 cm3
C. 252 cm3
D. 336 cm3
Answer: A. 84 cm3
Explanation:
0.42 g propanol + Na → H₂ gas. What volume of H₂ at RTP?
Propanol: C₃H₇OH, reacts:
C₃H₇OH + Na → C₃H₇ONa + ½H₂
Molar mass of C₃H₇OH = 60 g/mol
Moles = 0.42 / 60 = 0.007 mol
Moles H₂ = 0.007 × ½ = 0.0035 mol
Volume at RTP = 0.0035 × 24,000 = 84 cm³
✅ Answer: A
Question 4
Question: Permanent hard water may contain
dissolved magnesium sulfate, MgSO4. How many electrons are
present in a sulfate anion?
Options:
A. 46
B. 48
C. 49
D. 50
Answer: D. 50
Explanation:
- The
sulfate anion (SO42−) has:
- Sulfur
(S): 16 electrons
- Oxygen
(O): 4 × 8 = 32 electrons
- +2
extra e⁻ (due to charge)
- Total
electrons = 16 + 32 + 2 = 50 electrons (including the 2 extra
electrons from the charge).
The correct answer is D. 50.
Question 5
Question: Three orbitals j, k and l are
shown. What is the name of j, k and l?
Options:
A. Px, Py, Pz
B. s, Pz, Py
C. s, Px, Pz
D. s, Px, Py
Answer: D. s, Px, Py
Explanation:
- Based
on the diagram, j is the s-orbital, k is
the Px-orbital, and l is the Py-orbital.
Only s-orbital is spherical, others are dumbbell-shaped on x, y, z
axes.
- j = s
- k = px
- l = py
The correct answer is D. s, Px, Py.
Question 6
Question: The electronic configuration of an ion
is 1s22s22p63s23p63d3.
What is this ion?
Options:
A. Cr3+
B. Fe3+
C. Ni2+
D. Ti2+
Answer: A. Cr3+
Explanation:
Electronic config: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d³ → total 21 e⁻
- Cr:
atomic no. 24 → Cr³⁺ = 21 e⁻ ✅
✅ Answer: A
Question 7
Question: What are the shapes of the molecules
of methane and sulfur hexafluoride?
Options:
A. pyramidal, trigonal
B. pyramidal, octahedral
C. tetrahedral, trigonal
D. tetrahedral, octahedral
Answer: D. tetrahedral, octahedral
Explanation:
- Methane
(CH4) has a tetrahedral shape due to sp3 hybridization
(4 bond pairs, no lone pairs)
- Sulfur
hexafluoride (SF6) has an octahedral shape due
to sp3d2 hybridization (6 bond pairs)
- The
correct answer is D. tetrahedral, octahedral.
Question 8
Question: Which molecule has no overall dipole?
Options:
A. CH4
B. HCl
C. H2O
D. NH3
Answer: A. CH4
Explanation:
- CH4 is
a symmetrical molecule with no net dipole moment, non-polar ✅
- HCl, H2O,
and NH3 all have net dipole moments (polars) due
to their asymmetrical shapes.
- The
correct answer is A. CH4.
Question 9
Question: Which compound has the highest boiling
point and what is the intermolecular force that causes this boiling point to be
the highest?
Options:
A. ethanol, hydrogen bonds
B. chloromethane, permanent dipole
C. methane, Van der Waals
D. methane, hydrogen bonds
Answer: A. ethanol, hydrogen bonds
Explanation:
Highest boiling point & reason?
- Ethanol
has hydrogen bonding → strongest intermolecular force
- Others:
van der Waals or dipole only
- Ethanol
(C2H5OH) has hydrogen bonding, which is the
strongest intermolecular force, leading to the highest boiling point.
- The
correct answer is A. ethanol, hydrogen bonds.
Question 10
Question: “A lattice of positive ions surrounded
by delocalised electrons.” Which type of bonds does the statement best
describe?
Options:
A. co-ordinate bonds
B. covalent bonds
C. ionic bonds
D. metallic bonds
Answer: D. metallic bonds
Explanation:
- Metallic
bonds involve a lattice of positive ions surrounded by a sea of
delocalized electrons.
- The
correct answer is D. metallic bonds.
Question 11
Question: The gas laws can be summarised in the
ideal gas equation. A certain gas of mass 7.20 g is contained in a tank of
volume 5.00 dm33 at a pressure of 135 kPa and temperature of 42.5 °C.
Assume that the gas behaves as an ideal gas. What is the molar mass, Mr,
of the gas in the tank?
A. 1.85 g mol−1
B. 3.77 g mol−1
Answer: D. 35.8 g mol−1
Explanation:
Use ideal gas equation to
calculate molar mass (Mᵣ):
pV = nRT ⇒ n = pV/RT ⇒ Mr
= mass / number of moles
Given:
- p =
135 kPa = 135,000 Pa
- V =
5.00 dm³ = 0.005 m³
- T =
42.5 °C = 315.5 K
- R =
8.31 J mol⁻¹K⁻¹
- mass =
7.20 g
n = 135 000 x 0.005 / 8.31 x 315.5 = 675/ 2622.4045 ≈ 0.2575 mol
Mr
⇒ 7.20 / 0.2575 ≈ 28.0
✅ Answer: C
Question 12
Question: Which equation represents the standard
enthalpy change of formation of ethanol?
Options:
A. 2C(s)+3H2(g)+1/2O2(g)→C2H5OH(g)
B. 2C(s)+3H2(g)+1/2O2(g)→C2H5OH(l)
C. 4C(s)+6H2(g)+O2(g)→2C2H5OH(g)
D. 4C(s)+6H2(g)+O2(g)→2C2H5OH(l)
Answer: B. 2C(s) + 3H2(g) + 1/2O2(g)
→ C2H5OH(l)
Explanation:
- The
standard enthalpy change of formation refers to the formation of 1 mole of
a compound from its elements in their standard states.
- The correct equation is B, as it represents the formation of 1 mole of ethanol in its liquid state.
Question 13
Question: A reaction pathway is shown. Which row
is correct?
Options:
A. Q, U
B. Q, S
C. R, S
D. T, U
Answer: B. Q, S
Explanation:
- The
enthalpy change of the forward reaction is represented by Q.
- The
activation energy of the reverse reaction is represented by S.
- The
correct answer is B. Q, S.
Question 14
Question: The equation for the complete
combustion of methanol is shown. What is the enthalpy change of combustion of
methanol?
Options:
A. −966 kJ mol−1
B. −732 kJ mol−1
C. −234 kJ mol−1
D. +732 kJ mol−1
Answer: B. −732 kJ mol−1
Explanation:
- Using
Hess's Law, the enthalpy change of combustion is:
ΔHc=ΔHf(products)−ΔHf(reactants)
ΔHc = [(−394) + 2(−286)] − (−234) = −732 kJ mol−1
- The
correct answer is B. −732 kJ mol−1.
Question 15
Question: The reaction between acidified
potassium manganate(VII) ions, MnO4−, and
aqueous Fe2+ results in the manganate(VII) ions
being reduced to manganese(II) ions, Mn2+. What is the
correct equation for this reaction?
Options:
A. Fe2+ + MnO4−+ 8H+→ Fe3++Mn2++4H2O
B. 2Fe2+ + MnO4−+ 8H+→ 2Fe3++Mn2++4H2O
C. 10Fe2+ + MnO4−+ 8H+→ 10Fe3++Mn2++4H2O
D. 5Fe2+ + MnO4−+ 8H+ → 5Fe3++Mn2++4H2O
Answer: D. 5Fe2++ MnO4−+8H+→5Fe3++ Mn2++4H2O
Explanation:
Redox reaction: MnO₄⁻ oxidises Fe²⁺ to Fe³⁺.
- The
balanced redox equation is:
5Fe2++ MnO4−+
8H+ → 5Fe3++ Mn2++ 4H2O
Question 16
Question: Which reaction is not a redox
reaction?
Options:
A. 2Ca + O2 →2CaO2
B. Ca+2H2O→Ca(OH)2+H2
C. CaCO3→CaO+CO2
D. 2Ca(NO3)2→2CaO+4NO2+O2
Answer: C. CaCO3→CaO+CO2
Explanation:
Redox: look for change in oxidation number.
- In
reaction C, CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂
there is no change in oxidation states of any element, so it is not a redox reaction.
·
Ca stays +2, C stays +4, O stays −2 → no
redox
The correct answer is C.
Question 17
Question: Concentrated aqueous copper(II)
sulfate is electrolysed using copper electrodes. Which ionic half-equation
describes the reaction taking place at the cathode?
Options:
A. 2H++2e−→ H2
B. 4OH−→2H2O + O2 + 4e−
C. Cu → Cu2++ 2e−
D. Cu2++2e−→ Cu
Answer: D. Cu2++2e−→ Cu
Explanation:
- Electrolysis
of CuSO₄ using copper electrodes (Cu²⁺ gains electrons):
- At the
cathode, reduction occurs, and Cu2+ ions are
reduced to Cu.
- The
correct answer is D.
Question 18
Question: The reaction between hydrogen and
chlorine is reversible. Which conditions of concentration and temperature
favour the forward reaction?
Options:
A. add some hydrogen chloride, decrease the temperature
B. add some hydrogen chloride, increase the temperature
C. remove some hydrogen chloride, decrease the temperature
D. remove some hydrogen chloride, increase the temperature
Answer: D. remove some hydrogen chloride, increase
the temperature.
Explanation:
- According
to Le Chatelier's principle, removing HCl (a product) and
increasing the temperature (since the reaction is endothermic) will favour
the forward reaction.
H2 + Cl2 ⇌ 2HCl ∆H = + 49.7 (endothermic)
Favour forward reaction by:
- removing product (HCl)
- increasing temperature
- The
correct answer is D.
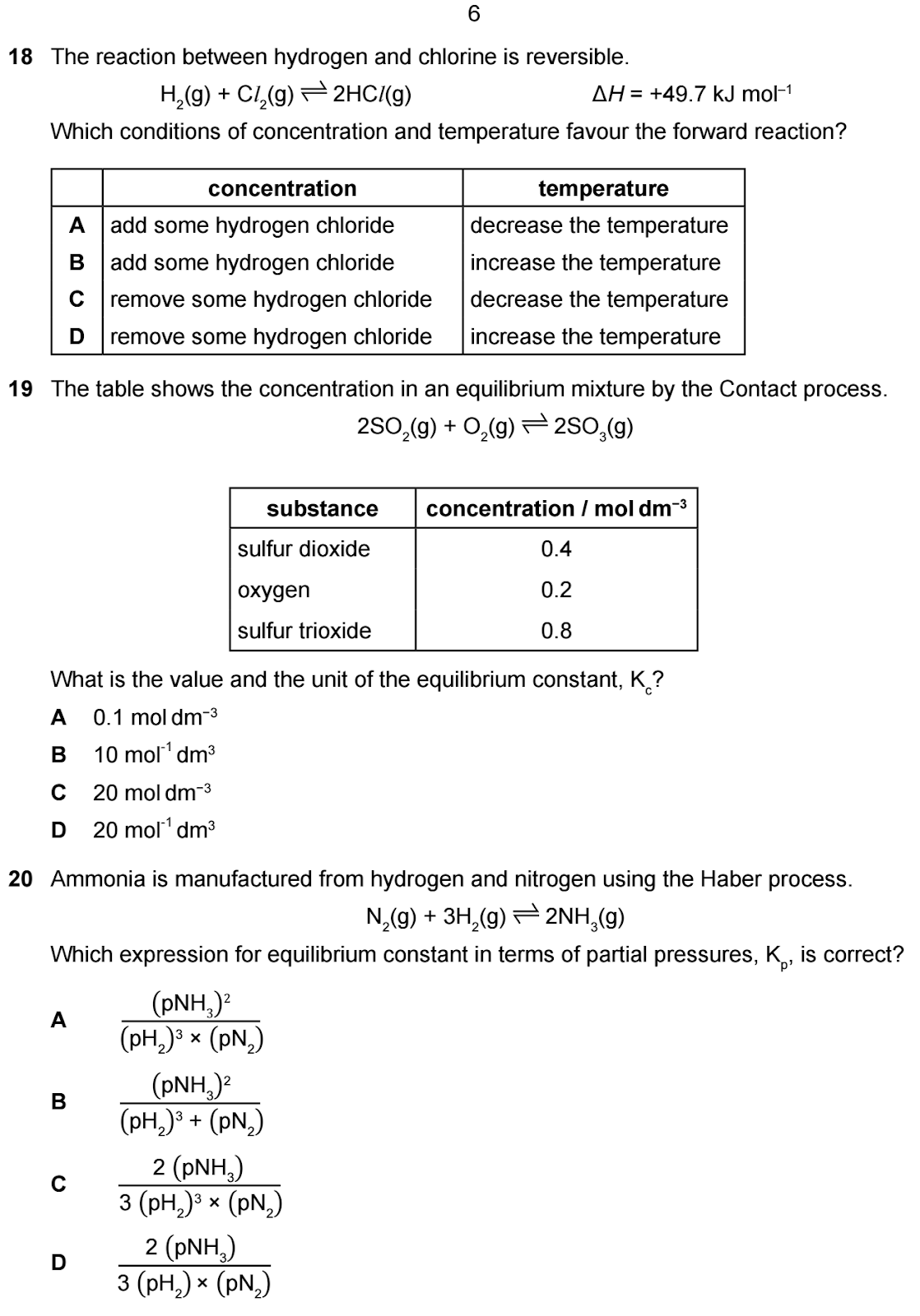
Question 19
Question: The table shows the concentration in
an equilibrium mixture by the Contact process. What is the value and the unit
of the equilibrium constant, Kp?
Options:
A. 0.1 mol dm−3
B. 10 mol−1 dm3
C. 20 mol dm−3
D. 20 mol−1 dm3
Answer: D. 20 mol−1 dm3
Explanation:
- The
equilibrium constant Kp is calculated as:
Kp = [SO3]2 / [SO2]2[O2] = 0.82 / 0.42 x 0.2 = 20 mol−1 dm3
Units: (mol/dm3)2/((mol/dm3)2×mol/dm3)
= mol−1dm3
✅ Answer: D
- The
correct answer is D.
Question 20
Question: Ammonia is manufactured from hydrogen
and nitrogen using the Haber process. Which expression for equilibrium constant
in terms of partial pressures, Kp, is correct?
Options:
A. (pNH3)2/(pH2)3 × (pN2)
B. (pNH3)2/(pH2)3 + (pN2)
C. 2(pNH3)/3(pH2)3 × (pN2)
D. 2(pNH3)3/(pH2) × (pN2)
Answer: A. (pNH3)2/(pH2)3
× (pN2)
Explanation:
- The equilibrium
constant Kp for the Haber process is:
Kp=(pNH3)2/(pH2)3
× (pN2)
- The
correct answer is A.
Question 21
Question: The equation shows the reaction of
sodium chloride with concentrated sulfuric acid. Which one is the conjugate
base for the forward reaction?
Options:
A. Cl−
B. HCl
C. HSO4−
D. H2SO4
Answer: C. HSO4−
Explanation:
- In the
forward reaction, H2SO4 donates
a proton (H+) to Cl−,
forming HCl and HSO4−.
- H₂SO₄
donates a proton → conjugate base is what remains → HSO₄⁻.
- The conjugate
base of H2SO4 is HSO4−.
Question 22
Question: Two reactions are shown. Both
reactions use catalysts. Which statement about the catalysts is correct?
Options:
A. Both reactions use a heterogeneous catalyst.
B. Both reactions use a homogeneous catalyst.
C. Reaction 1 uses a heterogeneous catalyst and reaction 2 uses a homogeneous
catalyst.
D. Reaction 1 uses a homogeneous catalyst and reaction 2 uses a heterogeneous
catalyst.
Answer: A. Reaction 1 uses a heterogeneous
catalyst and reaction 2 uses a heterogeneous catalyst.
Explanation:
- Reaction
1 (Contact process) uses a heterogeneous catalyst (vanadium(V) oxide).
- Reaction
2 (Haber process) uses a heterogeneous catalyst (iron).
- Contact process (SO₃): solid V₂O₅ → heterogeneous
- Haber process (NH₃): iron solid → heterogeneous
✅ Answer: A
Question 23
Question: The Boltzmann distribution shows the
distribution of the kinetic energy of molecules at a constant temperature. The
temperature is increased by 10K. Which row is correct?
Options:
A. the peak is at a lower height, size of the area labelled Y decreases
B. the peak is at a lower height, size of the area labelled Y increases
C. the peak remains the same height, size of the area labelled Y decreases
D. the peak remains the same height, size of the area labelled Y increases
Answer: B. the peak is at a lower height, size
of the area labelled Y increases
Explanation:
- When
temperature increases, the peak of the Boltzmann distribution shifts to a
lower height, and the area under the curve (Y) increases.
Boltzmann distribution: increasing T → curve flattens, peak shifts right
So:
- peak is lower
- area Y (Ea) increase
- The correct answer is B.
Question 24
Question: Which property is shown in graph S and
graph T?
Options:
A. melting point, ionisation energy
B. melting point, atomic radius
C. atomic radius, melting point
D. ionisation energy, electronegativity
Answer: B. melting point, atomic radius
Explanation:
- Graph
S shows melting point, and graph T shows atomic radius.
- The
correct answer is B.
Question 25
Question: Which period 3 chloride dissolves in
water and gives a solution of pH 7?
Options:
A. Al2Cl6
B. PCl5
C. NaCl
D. SiCl4
Answer: C. NaCl
Explanation:
- NaCl is
a neutral salt that dissolves in water to give a solution with pH 7.
- The
correct answer is C.
Question 26
Question: An aqueous solution contains both
barium and calcium ions. Aqueous sodium hydroxide and dilute sulfuric acid are
added to separate portions of this solution. Which row shows the precipitate
formed?
Options:
A. barium hydroxide, barium sulfate
B. barium hydroxide, calcium sulfate
C. calcium hydroxide, barium sulfate
D. calcium hydroxide, calcium sulfate
Answer: C. calcium hydroxide, barium sulfate
Explanation:
- NaOH reacts
with Ca2+ to form Ca(OH)2 (calcium
hydroxide), which is insoluble.
- H2SO4 reacts
with Ba2+ to form BaSO4 (barium
sulfate), which is insoluble.
·
OH⁻: both Ba²⁺ and Ca²⁺ form precipitates of hydroxides
·
H₂SO₄: Ba²⁺ forms insoluble BaSO₄, CaSO₄ is more soluble
Question 27
Question: A sample of zinc nitrate is heated in
the apparatus as shown. A mixture of gases is released. The mixture is then
tested with a glowing splint. What are the results?
Options:
A. colourless, extinguished
B. brown, extinguished
C. colourless, relights
D. brown, relights
Answer: D. brown, relights
Explanation:
- When
zinc nitrate is heated, it decomposes to produce NO2 (brown
gas) and O2 (colourless gas).
- The
glowing splint relights in the presence of O2.
Zinc nitrate decomposes → ZnO (solid) + NO₂ (brown) + O₂
- Brown gas
- Oxygen supports glowing splint → relights
- The
correct answer is D.
Question 28
Question: The Group 17 elements chlorine,
bromine and iodine have different colours. Which row shows the correct colour
of the Group 17 elements when in a vapour state?
Options:
A. green, purple, red-brown
B. green, red-brown, purple
C. purple, red-brown, green
D. red-brown, green, purple
Answer: B. green, red-brown, purple
Explanation:
- Chlorine
gas is green, bromine vapour is red-brown, and iodine vapour is purple.
Question 29
Question: What happens when chlorine is bubbled
through aqueous potassium iodide?
Options:
A. Iodide ions are oxidised to iodine.
B. Chlorine is oxidised to chlorate(V) ions.
C. Chlorine is oxidised to chloride ions.
D. There is no observable reaction.
Answer: A. Iodide ions are oxidised to iodine.
Explanation:
- Chlorine
is more reactive than iodine and will oxidise iodide ions (I−)
to iodine (I2).
·
Cl2 is more reactive → displaces I2:
·
Cl2 + 2I− → 2Cl−
+ I2
·
I⁻ is oxidised to I2.
- The
correct answer is A.
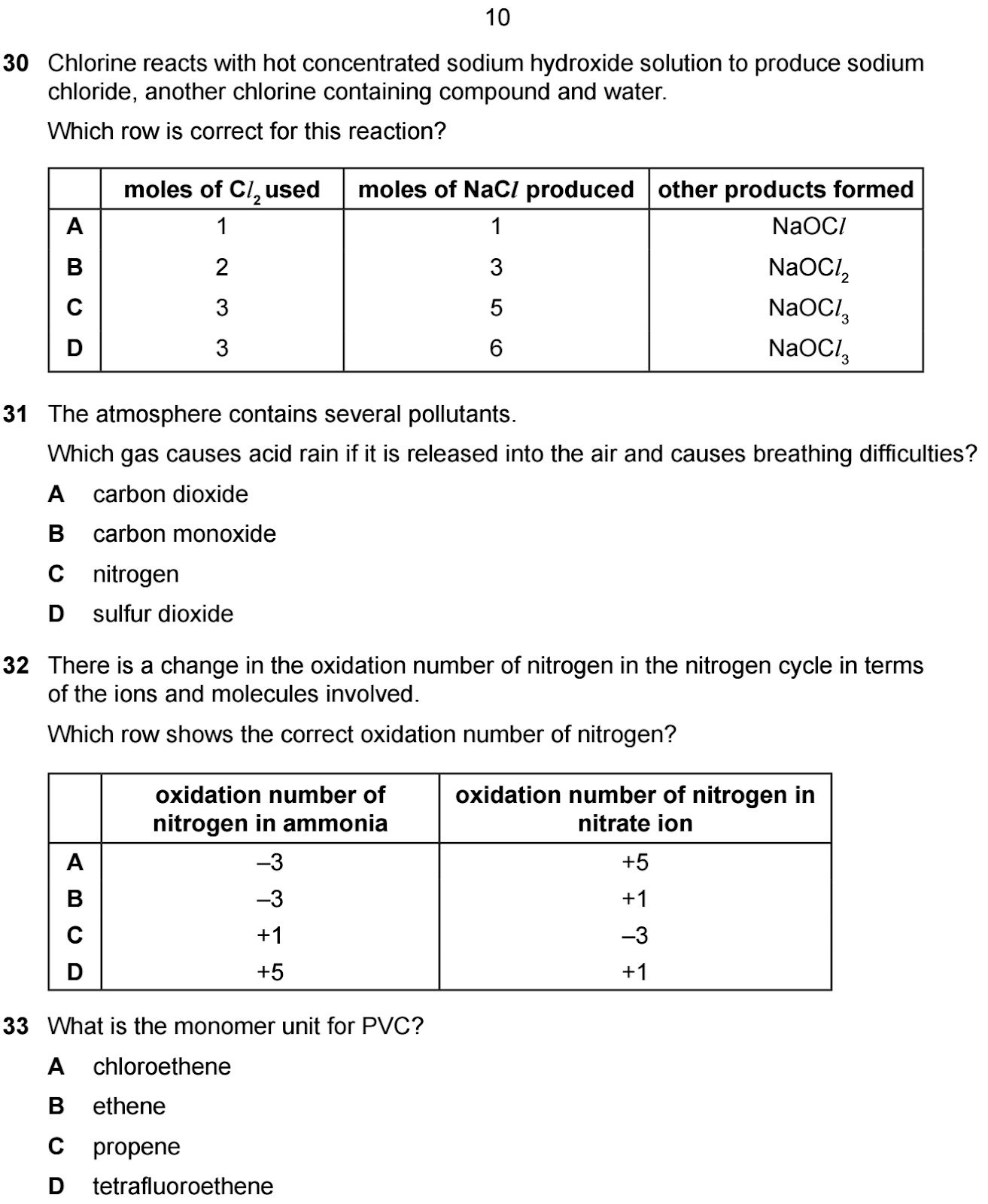
Question 30
Question: Chlorine reacts with hot concentrated
sodium hydroxide solution to produce sodium chloride, another chlorine
containing compound and water. Which row is correct for this reaction?
Options:
A. 1, 1, NaOCl
B. 2, 3, NaOCl2
C. 3, 5, NaOCl3
D. 3, 6, NaOCl3
Answer: A. 1, 1, NaOCl
Explanation:
- The
reaction is:
Cl2 +
NaOH → NaCl + NaOCl +
H2O
So: 1 mol Cl2 → 1 mol
NaCl (Balanced Equation)
- 1 mole
of Cl2 produces 1 mole of NaCl and
1 mole of NaOCl.
- The correct answer is A.
Question: The atmosphere contains several
pollutants. Which gas causes acid rain if it is released into the air and
causes breathing difficulties?
Options:
A. carbon dioxide
B. carbon monoxide
C. nitrogen
D. sulfur dioxide
Answer: D. sulfur dioxide
Explanation:
- Sulfur
dioxide (SO2) reacts with water in the atmosphere to
form sulfuric acid, causing acid rain. It also causes breathing
difficulties. SO₂ forms acid rain and causes respiratory
issues
- The
correct answer is D.
Question 32
Question: There is a change in the oxidation
number of nitrogen in the nitrogen cycle in terms of the ions and molecules
involved. Which row shows the correct oxidation number of nitrogen?
Options:
A. -3, +5
B. -3, +1
C. +1, -3
D. +5, +1
Answer: A. -3, +5
Explanation:
- In
ammonia (NH3), nitrogen has an oxidation number of -3.
- In
nitrate ions (NO3−), nitrogen has an
oxidation number of +5.
- The
correct answer is A.
Question: What is the monomer unit for PVC?
Options:
A. chloroethene
B. ethene
C. propene
D. tetrafluoroethene
Answer: A. chloroethene
Explanation:
- PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is made from the monomer chloroethene (CH2=CHCl).
- The correct answer is A.
Question 34
Question: A reaction occurs when a sample of
2-bromopropane is heated under reflux with potassium hydroxide dissolved in
ethanol. Which row is correct?
Options:
A. elimination, propan-1-ol
B. elimination, propene
C. substitution, propan-1-ol
D. substitution, propene
Answer: B. elimination, propene
Explanation:
- Heating
2-bromopropane with KOH in ethanol leads to an
elimination reaction, producing propene.
- 2-bromopropane
+ KOH (ethanol) → elimination → alkene (propene)
- The
correct answer is B.
Question 35
Question: When an organic compound F is treated
with hot aqueous acid, two compounds are formed. Which two structures show the
compounds formed?
Options:
A. CH3CH2CO2H+CH3CH2CH2OH
B. (CH3)2CHCO2H+CH3CH2CH2OH
C. CH3CH2CO2H+CH3CH(OH)CH3
D. (CH3)2CHCO2H+CH3CH(OH)CH3
Answer: C. CH3CH2CO2H+CH3CH(OH)CH3
Explanation:
- The
compound CH3CH2CO2CH(OH)2 undergoes
hydrolysis to form propanoic acid (CH3CH2CO2H)
and isopropanol (CH3CH(OH)CH3).
CH₃CH₂CO₂CH(CH₃)₂ is an ester → acid hydrolysis gives:
- acid: CH₃CH₂COOH
- alcohol: CH₃CH(OH)CH₃
- The
correct answer is C.
Question: Which compound does not show
geometrical isomerism?
Options:
A. CBr(CH3)=CH2
B. CBr(CH3)=CBr(CH3)
C. CH(CH3)=CH(CH2CH3)
D. CH(CH3)=CH(CH2CH2CH3)
Answer: A. CBr(CH3)=CH2
Explanation:
- Geometrical
isomerism requires two different groups on each carbon of the double
bond. CBr(CH3)=CH2 does not meet this
requirement.
Geometrical isomerism needs C=C with different groups
- A: CH₂=C(CH₃)Br → only 1 H → no
cis-trans
- B: CBr(CH₃)=CBr(CH₃) → has
cis-trans
- C: CH(CH₃)=CH(CH₂CH₃) → yes
- D: yes
- The
correct answer is A.
Question 37
Question: How many chain isomers have the
molecular formula C4H10?
Options:
A. 2
B. 3
C. 5
D. 6
Answer: A. 2
Explanation:
- C4H10 has
two chain isomers: butane and 2-methylpropane.
- The
correct answer is A.
Question 38
Question: The molecular formula of compound Y
is C6H14O. Compound Y can react with alkaline aqueous iodine to
form tri-iodomethane. What could be the identity of compound Y?
Options:
A. CH3CH2CH2COH(CH3)2
B. CH2(OH)CH2CH(CH3)2
C. CH3CH2CH(OH)CH(CH3)2
D. CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2CH2OH
Answer: C. CH3CH2CH(OH)CH(CH3)2
Explanation:
- The
iodoform test is positive for compounds with the structure CH3CH(OH)R.
- Triiodomethane
test → needs CH₃CO– or CH₃CH(OH)–
Only option C has a secondary alcohol with CH₃–C(OH)– - The
correct answer is C.
Question 39
Question: Which types of stereoisomerism are
shown by 1,2-dichloroethene?
Options:
A. both geometrical and optical isomerism
B. geometrical isomerism only
C. neither geometrical isomerism nor optical isomerism
D. optical isomerism only
Answer: B. geometrical isomerism only
Explanation:
- 1,2-dichloroethene can exhibit geometrical isomerism (cis/trans) but not optical isomerism (no chiral center).
- The correct answer is B.
Question 40
Question: Aldehydes and ketones are produced by
the oxidation of either primary or secondary alcohols. Which row is correct?
Options:
A. aldehydes, ketones
B. ketones, aldehydes
C. aldehydes, aldehydes and ketones
D. ketones, aldehydes and ketones
Answer: A. aldehydes, ketones
Explanation:
- Primary
alcohols oxidise to aldehydes, and secondary alcohols oxidise to ketones.
·
Primary alcohol → aldehyde → carboxylic acid
·
Secondary alcohol → ketone only












Comments
Post a Comment